Carbon Fibre Guides or Ball Bearings?
The choice between a ball-bearing rotary joint or one supported by a carbon guide is affected by several factors, let's find out which ones.
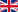
Both options feature a self-supporting structure that is used when there is no external structure to mount a rotary joint, or when the joint configuration and application do not require external support. For many applications, rotary joints with external ring support, such as the PTX® rotary joint or the CorrPro® rotary joint, are the best solution.
Self-supporting KADANT rotary joints
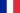
Carbon-supported rotary joints, such as the SX® rotary joint or the ELS™ rotary joint, are best suited for low-speed and high-temperature applications. Carbon has a low coefficient of thermal expansion and can therefore tolerate a wide temperature differential.
KADANT rotary joints with Carbon guides
The rotary joint fitting will have about the same temperature as the fluid and will heat up very quickly causing it to expand. The body of the rotary joint heats up more slowly and is generally cooler due to exposure to atmospheric conditions. Additional clearance is only required on the guide ID to handle the thermal expansion. In a bearing-supported rotary joint, the guide ID and OD are closely coupled and the thermal expansion must be absorbed by the bearing's internal clearance. This makes the configuration and choice of bearing dependent on temperature.
Carbon rails also have some advantages in larger sizes. Carbon is easily custom shaped, whereas large ball bearings can be more difficult to source, sometimes requiring long lead times. Carbon guides do not require lubrication and only need maintenance under normal conditions when the seal ring is worn and needs to be replaced. Carbon-supported rotary joints range in size from ½" to 14" flow diameter.
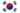
JOHNSON-FLUITEN rotary joint with ball bearings
Ball bearing-supported joints, such as the RX® rotary joint and the SERIES R joint, are typically used in high-speed applications and when runout is critical. Rotary joints operating at high speeds utilise a balanced face seal that requires precise alignment of the seal faces. In addition to face seals, multi-pass rotary joints with DuraSeal® technology require runout control that only ball elements can provide. Ball bearings are also used in applications requiring low drive torque. Some applications require a relubrication and maintenance programme to ensure optimum service life. Ball bearing rotary joints are available in a wide range of sizes, the largest of which are typically suitable for customised applications.
Are you interested in finding out what is the best solution for your machine? Discover the KADANT proposals that can be provided by Johnson-Fluiten S.r.l, contact us for advice from one of our experts!