Maintenance 4.0: how to reduce downtime with Quick Replacement Design
Today, maintenance is no longer a reactive function. It is a design variable that directly affects productivity, reliability, and overall operating costs. This is especially true for critical components, such as rotary joints, used to transfer water, steam, thermal oil, and other industrial fluids in continuous applications that are strategically important for production.
When a rotary joint stops or leaks, the impact is rarely limited to the component: even a short machine downtime affects production, quality, and safety. It is in this context that the concept of Maintenance 4.0 takes on concrete meaning.
Why is the maintenance of rotary joints a critical issue?
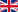
In many plants, rotary joints are perceived as standard components. The problem arises when it becomes necessary to replace the mechanical seal, which is often designed to be accessed only after the joint has been removed from the machine.
This approach typically involves:
- - longer than necessary downtime,
- - invasive work on shafts and connections,
- - a higher probability of errors during reassembly.
In sectors such as paper, plastics, food, chemicals, and machine tools, this approach is no longer sustainable.
What is the role of mechanical seals in a rotating joint?
The mechanical seal is the most stressed component of the rotary joint. It operates under thermal loads, variable pressures, and high rotational speeds. Its wear is physiological, but what makes the difference is how its replacement has been designed.
A seal that is difficult to replace turns a normal maintenance operation into a critical event for the plant.

What is Quick Replacement Design (QRD)?
Quick Replacement Design is a design solution developed by Johnson-Fluiten thanks to the know-how gained through collaboration with Fluiten S.p.A., a specialist in the design of mechanical seals.
The principle is simple but important: the mechanical seal can be replaced easily without removing the rotating joint from the machine.
This approach transforms what is traditionally a long and complex operation into a quick, controlled, and repeatable task that can be performed even by those without specific training.
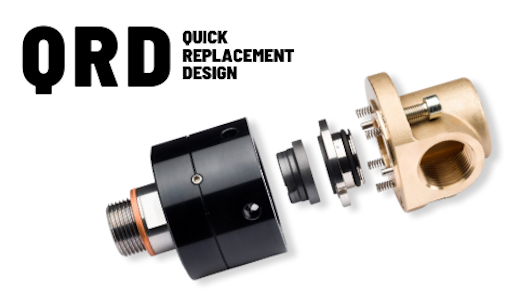
What are the concrete advantages of Quick Replacement Design?
The advantage of QRD is clear from an operational point of view. The main benefits are:
- Reduced downtime - Replacing the seal takes minutes rather than hours.
- Simplified maintenance- There is no need to dismantle the joint or work on adjacent parts of the system.
- Greater operational safety - Fewer invasive operations reduce the risk of errors and damage.
- Greater production continuity - Interventions can be planned without significant impact on the production cycle.
These advantages are particularly relevant for highly saturated or continuously operating systems.
How does QRD fit into Maintenance 4.0?
Maintenance 4.0 combines intelligent design, rapid response, and immediate access to information. QRD fully responds to this logic because it reduces Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) and makes maintenance predictable.
This is accompanied by a second key element: the digitization of field information.
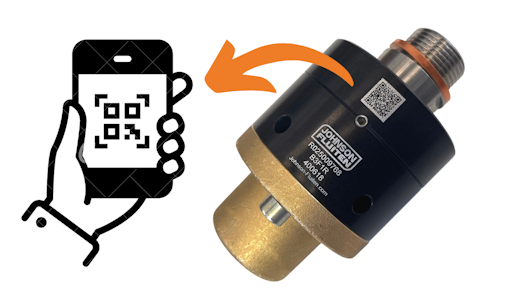
Why is the QR code engraved on the joint part of smart maintenance?
Every Johnson-Fluiten rotary joint has a QR code laser-engraved on the body of the component. Scanning it gives you direct access to specific product information, eliminating intermediate steps.
Specifically, the QR code allows:
- immediate access to up-to-date technical documentation,
- quick identification of the model and configurations,
- correct and safe reordering of spare parts.
This tool is particularly appreciated by maintenance technicians, engineers, and purchasing managers.
What maintenance options are available?
Johnson-Fluiten takes a flexible approach, allowing customers to choose the maintenance model that best suits their organization.
The two main options are:
- Self-maintenance with spare parts kits
For R and RH rotary joints, typically used for water and oil in cylinder heating, the kits include complete mechanical seals and, if necessary, lifetime greased bearings for high temperatures. Thanks to the QRD, the work can be carried out quickly without dismantling the joint.
- Johnson-Fluiten full-service
The customer returns the joint, which is overhauled, tested, and returned in like-new condition. This solution is often preferred by OEMs and machine builders for larger or custom joints.
In both cases, the goal is to minimize downtime while maintaining high joint performance.

Why is QRD a lifecycle investment?
Choosing a rotary joint with Quick Replacement Design means thinking in terms of total cost of ownership, not individual components. QRD reduces downtime, simplifies maintenance, and makes the plant more resilient.
It is this logic that distinguishes a simple supplier from a technical partner focused on operational continuity.
Adopting rotary joints designed from the outset for quick and controlled maintenance means addressing one of the main causes of unplanned machine downtime. It is not just a matter of reducing the time needed to replace a mechanical seal, but of making the plant more resilient, less dependent on extraordinary interventions, and easier to manage in the long term.
For this reason, choosing solutions designed for maintenance is not an isolated technical decision, but a strategic assessment of the overall reliability of the machine and the plant.
Essential technical glossary on rotary joints and industrial maintenance
To make the content understandable even to those who do not work with the component on a daily basis, below is a selection of the main technical terms used in the article.
Rotary joint
Mechanical component that allows the transfer of fluids (water, steam, oil, air, special fluids) from a fixed part to a rotating part, maintaining the seal and separation from the external environment.
Mechanical seal
Sealing system consisting of coupled surfaces that prevent fluid from escaping from the rotary joint. It is the part most subject to wear and one of the main variables that determine the reliability of the component.
Downtime
Period of inactivity of a machine or plant. It can be planned (scheduled maintenance) or unplanned (sudden failure or loss).
Quick Replacement Design (QRD)
A design solution that allows the mechanical seal of a rotary joint to be replaced without removing the component from the machine, drastically reducing maintenance time and complexity.
Spare parts kit
A set of components supplied by the manufacturer for the maintenance of the rotary joint. It may include mechanical seals, gaskets, springs, and bearings, selected according to the model and application.
MTTR (Mean Time To Repair)
An indicator that measures the average time required to repair a component or system after a failure. A low MTTR indicates faster and more efficient maintenance.
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
The total cost of owning a component or machine, which includes not only the purchase price, but also maintenance, downtime, spare parts, and management costs over time.
Maintenance 4.0
An advanced approach to industrial maintenance that integrates component design, information digitization, rapid response, and structural reduction of downtime.
Did you like this article?
- Find out more: Visit the products area to explore our solutions
- Contact us: Do you have a sealing problem? Request a technical analysis today info-jf@johnson-fluiten.com / +39.023394091
Autore dell’articolo